Atm devices
Introduction
Degree of efficiency of equipment for the production of thermal energy by combustion depends of unit capacity. This means that the production process for consumers with variable demand will end up with higher consumption of primary fuels (coal, oil, gas, etc..). This fact is of particular importance in thermotechnical installations (heating, ventilation, etc.) working with hot water and whose consumption is changing from practically zero to a maximum value and where most of the time installation is working with a much lower consumption of installed capacity boilers. This fact can best be seen if we compare the values of efficiency of boiler unit Vk and boiler efficiency installations annually Vi.
For example boilers for liquid / gas tank:
Vk = cca 0,9
Vi = cca 0,7
for coal-fired boilers:
Vk = cca 0,8
Vi = cca 0,55
To adjust hot water production and consumption, in addition to other methods like adding number of industrial boilers, burners etc, probably the most effective is use of accumulator because:
– applying accumulators boilers operate in the most favourable mode, regardless of the level of consumption
– excess energy produced is stored in the accumulator so in the downtime (boilers standby mode, furnaces) is brought to the consumer.
The above example shows one of the possibilities of application of the accumulator. For this and similar purposes Termo Simax offers devices “Atm”.
Composition, Structure And Connections
Atm devices are steel vessels in which membrane, that separates vessel space into two compatible parts, is embedded. In vessel separated like this first part is filled with cold water (water that has gone through cycles of cooling to the consumer), and the second part is filled with heated water (water that has gone through cycles of heating boiler), where each other can not significantly interfere.
Of course, the question is, why membranes in the vessel, and why not regular storage tanks of hot water? The answer is given trough consideration of circulating hot water system scheme. Namely, the system consists of two rounds of the fluid at different temperature levels:
– round of heated water that has undergone heat source,
– circuit of cooled water which has undergone consumers.
For vessels without membranes, both circles meet on the same spot, which leads to great difficulties in the process of warming up and heating. Also, it is practically impossible to change fluid in the entire volume of one-piece vessels in case of simultaneous flow of water. For these reasons, application of accumulators without membrane where not usable which led to withdrawal from use in energetics. Installation of the membrane in the accumulators resolve these issues.
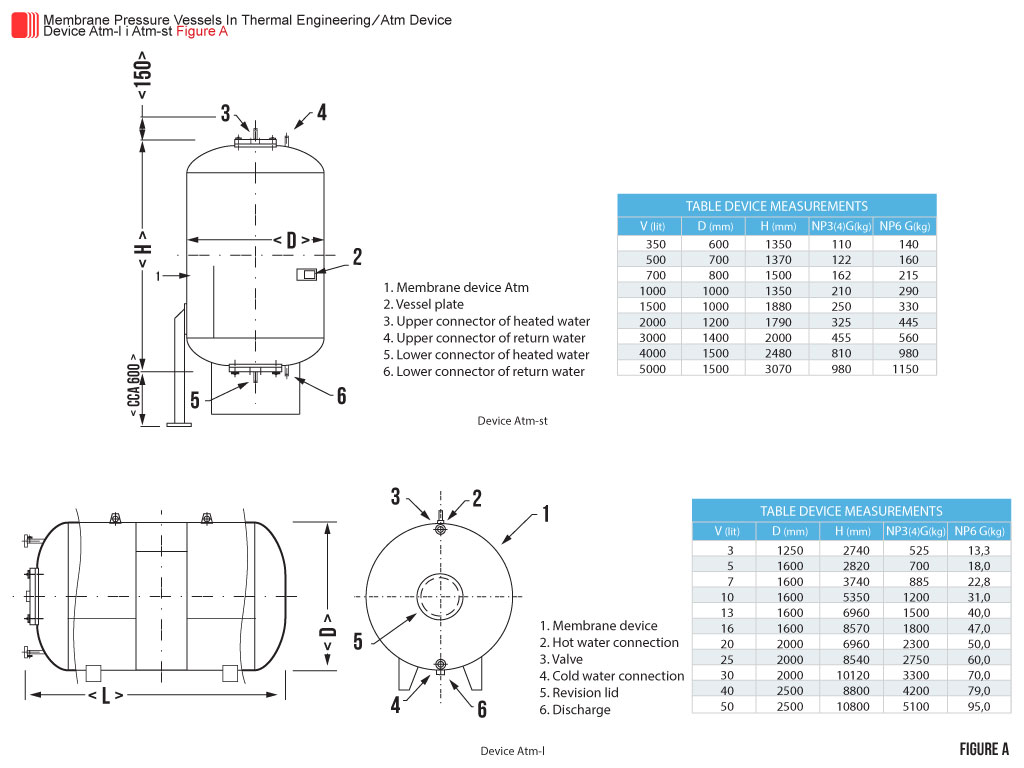
Atm devices are manufactured as vessels of structural steel in the vertical from 350l to 5000l, and horizontal from 3m³ to 100m³ volume, for a nominal pressure NP4 bar (other sizes and pressures – on request). Membrane vessels for water temperatures up to 110°C (higher temperatures on request). Devices have revision opening through which one can intervene and if necessary replace the membrane. The devices are isolated and protected from the outside depending on location (laying underground, aboveground installation, exterior, interior etc).
Losses of Termo–Simax's devices are approximately 3% to 4% of annual consumption. Appearance, dimensions and measures devices, and connectors can be seen in figure A.
Modes Of Operation
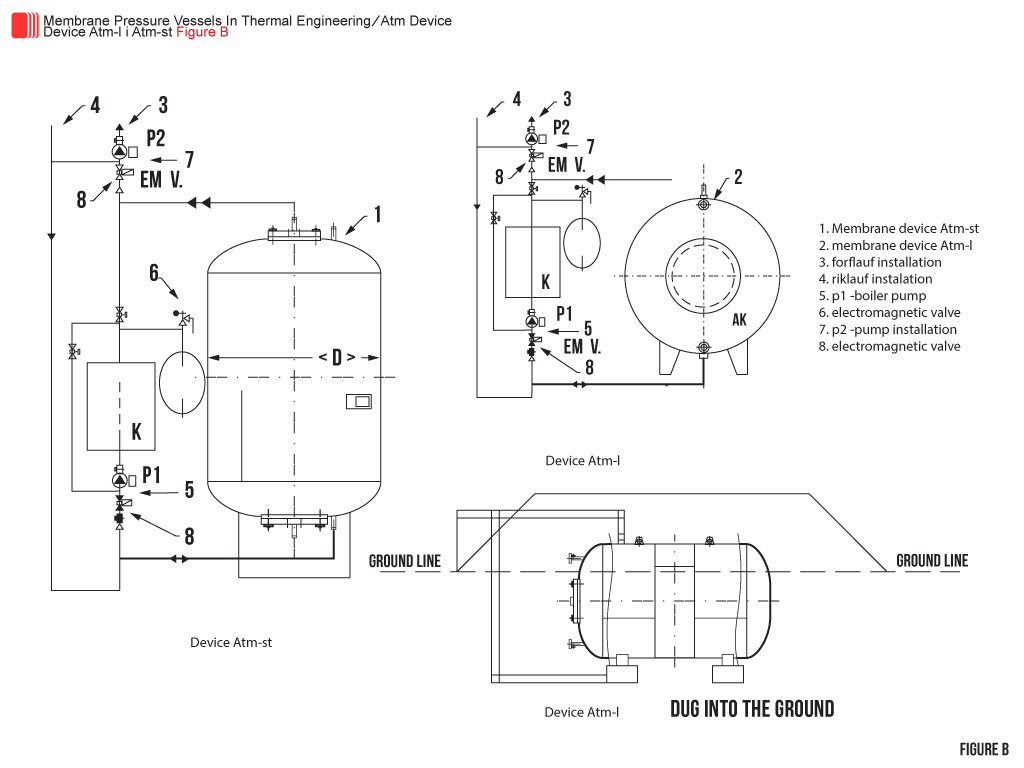
Atm devices are connected in parallel with the consumer installation figure B. Their running consists of two circulating rounds and is regulated by two regulatory circuits from which first regulates charge of accumulator (boiler circuit) and second consumption (circle of consumers). The work is performed in a way that hot water boilers distributed simultaneously to both consumers and accumulator. and any excess heat that is greater than the immediate consumption is stored in the accumulators storage space until it is full. It stops by thermostat – gas, oil, or suspension of operation – coal and consumers continue to be powered exclusively with accumulators until runs out, and then the cycle repeats.
Size Selection And Application Of Accumulator
The choice of accumulator size is closely related for its application. The device can be designed for:
– accumulation (hourly, daily, weekly, etc.),
– for primary fuel savings,
– expanding the capacity of existing heat sources,
– use of waste heat, etc…
Regardless of the application, its capacity (charge) is determined by the water content of the court Vak water temperature during charging twk and average temperature of return consumers water tw" during the emptying cycle:
Qak= Vak · Cp · (twk - tw") = (W);
Cp= 1,16 W/kg, °C
According to this equation, for a particular purpose, we select accumulator sizes. Thus, approximate equation are given for size selection and specific purpose.
Basic applications of accumulators in thermoenergetics:
1. Reduction in primary fuels consumption
Annual savings to be expected:
For gas – up to 15%
For liquid fuels – up to 20%
For coal – up to 35%
2. Utilization of low–rate electric power in electro–boilers
By using accumulators the consumption ratio between high and low–rate electricity which stands at approximately 80% to 20% (high to low) can be reversed to become 20% to 80% (high to low).
3. Maxigraph "ironing" when electric power is used
The operation mentioned above provides the cheapest energy that can be used for the heating of different objects.
4.Expansion of existing boiler rooms Qki=(Kw) when the operation of equipment is prolonged in non–working time
This way consumer installations can be enlarged without the increase in energetics and the switch from stronger fuels (gas, petroleum) onto less potent ones (coal) becomes feasible.
5.Reduction of participations (capital expenses) to distributors (electric power and gas) through one–time "registry power" reduction Qiv=(Kw)
This operation reduces "registry power" and energy consumption which is very important to investors as well as to energy (electric power and gas) providers.
6. Accumulation of "refuse" thermal energy from industrial and other processes which is realized either through water or with the use of another carrier (thermal oil, steam and the like).
7. With the usage of many different energy sources (coal and electric power, coal and liquid fuels and so on).
8. With the combustion of fuels of variable heat power such as bio-mass, wood waste etc.
9. Accumulation of solar energy applied in different consumption systems that use hot-water such as heating system and preparation of sanitary hot–water.
Ordering
When ordering, it is necessary to indicate the size and type of unit, nominal pressure and connectors, if it is under the standard program and Figure A, and if not, the main and volume measures too. Vessels are shipped without isolation and they are formed by the user.



